BERKELY PRIZE TEACHING FELLOWSHIP
TEACHING UNIVERSAL DESIGN
DEDICATED TO ELAINE OSTROFF, HONORARY AIA, CO-FOUNDER OF ADAPTIVE ENVIRONMENTS, BOSTON, MASSACHUSETTS, USA.
The term "Universal Design" has evolved from "Barrier Free Design", "Accessible Design", "Transgenerational Design", and "Adaptable Design". It is now considered to be synonymous with "Design for All" and "Inclusive Design." (Universal Designers & Consultants, Inc. (UD&C), publishers of UniversalDesign.com)
Design for All is design for human diversity, social inclusion and equality. (EIDD Stockholm Declaration, 2004).
We have defined Inclusive Design as: design that is inclusive of the full range of human diversity with respect to ability, language, culture, gender, age and other forms of human difference. (Inclusive Design Research Centre)
Starting in 2013, the BERKELEY PRIZE Committee broadens the scope of the activities of the PRIZE by offering faculty who teach undergraduate architectural design an academic-year Teaching Fellowship. The primary goal for the BERKELEY PRIZE Teaching Fellowship is to focus students’ attention on the social and physical characteristics of the proposed users of the buildings and spaces they design.
This is anticipated to be an annual competition. As prior years’ results become available, it is hoped to build on what was accomplished in the preceding year(s) – particularly, what standards the previous Fellows set for excellence. It is hoped that those who apply will address and integrate the successes from previous years into their curricula proposals and proposed teaching.
We are looking for the widest range of proposals for teaching Universal Design. This year, to reflect the BERKELEY PRIZE topic of the Architect and the Accessible City, the emphasis could be placed on a specific client group: those with physical and mental disabilities. This includes the disabled who use the building or space, those who visit the building, and those in the general public who might, at a future time, need to be accommodated. (Important: Go to the Student Proposals page for all of this year’s semifinalist proposals highlighting the student’s views of what the Accessible City means.)
At the same time, your proposal might address another client group altogether, or address a design issue other then buildings. Your specific and unique approach to tackling the complex issue of Universal Design should be at the heart of the Fellowship application. In your proposal you agree to teach the studio(s) you are now teaching, but now taught with an emphasis on Universal Design.
The award of the BERKELEY PRIZE Teaching Fellowship will be based on a number of factors (see, “To Enter”, for more details). In the end, the decision will be based on what makes your proposed approach more likely to succeed than that from other applicants. How exactly will your teaching involve those with disabilities, for instance, either as critics, field trips, consultants, or through rigorously directed readings? What goals are you hoping to achieve and how will you evaluate the results? What makes this course a new way at looking at the design of buildings and spaces, not just a gloss of more typical, formal (geometric) building design curricula?
In essence: How does your course best reflect the ideals of the social art of architecture?
|
|
|
 Like everyone else, this worker in Mexico needs transportation to his job. Public transport needs to be accessible for persons with mobility, sensory, and cognitive disabilities.  Persons with disabilities around the world are promoting transport systems that provide mobility for everyone. Mexican disability advocates are shown meeting with local transit officials to promote accessible transport. AEI has published guides to assist planners and advocates of inclusive transportation.  An accessible travel chain begins with safe streets and sidewalks. This street in Foshan, China, has separate rights-of-way for pedestrians, human-powered vehicles, and motor-powered vehicles.  Disability advisors at Rio de Janeiro’s Independent Living Center monitored access features for this street crossing, part of the Rio City Project.  Tactile guideways and tactile warning strips assist blind and sight-impaired pedestrians as well as others in Foshan, China.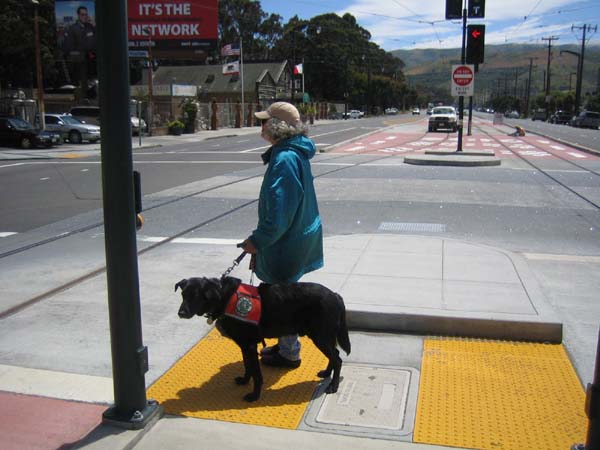  Tactile warnings alert this blind person crossing a mid-street island in San Francisco, USA.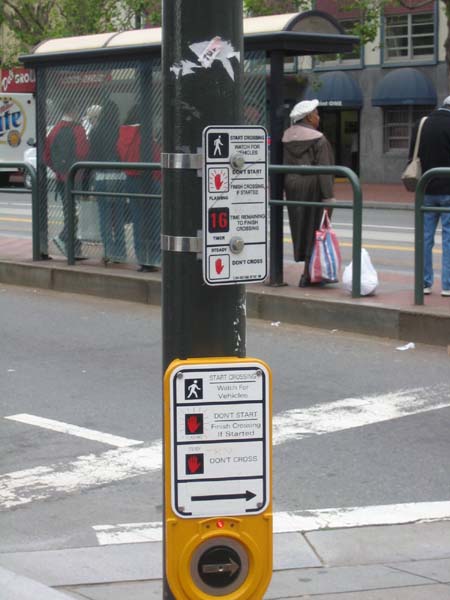  Busy intersections benefit from pedestrian controlled buttons and assist blind persons to cross through sound and vibration signals  Tactile warnings protect blind persons – and all other passengers – from getting too close to the platform edge in transit stations.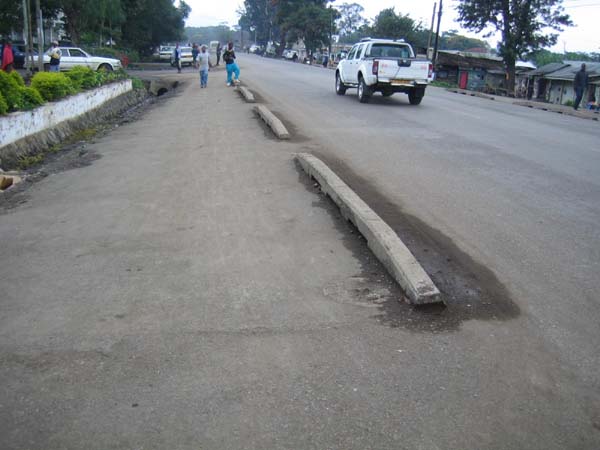  This footway adjacent to a road in Tanzania is protected by curb pieces which separate motor traffic from pedestrians and bicycles. Such basic safety measures are needed to prevent pedestrian injuries along roadways in many countries.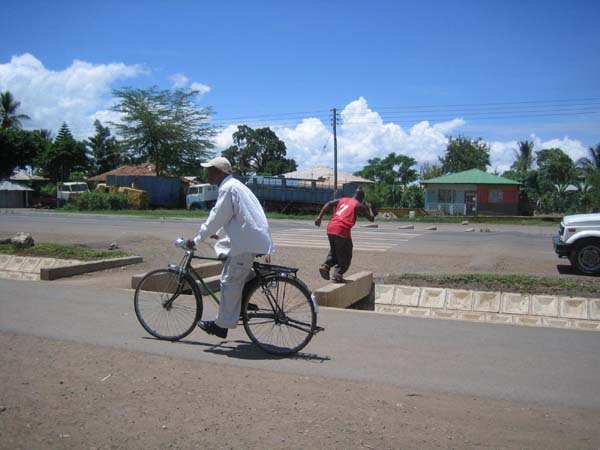  Even better, pedestrian and non-motorized traffic can be kept safely removed from motorized traffic by accessible sidewalks separated from the roadway, in this case by a well-designed drainage system along a main road in Tanzania. Speed bumps are used to slow traffic at crosswalks.  This pedestrian crosswalk provides level access to a bus island at an inter-modal transfer center in Mexico City.
Photo by T. Rickert, courtesy of DFID (UK) and TRL (UK).  Ticket vending machines should be low enough for use by wheelchair users and all short persons, as illustrated by the good design of this machine at a BART station in the San Francisco Bay area, USA.  Stairs are often retrofitted with stair lifts in transit terminals, as here in a Tokyo subway station. However, in new construction, elevators should be considered where possible.  A wheelchair user takes the elevator from the platform level of the Shenzhen, China, railroad station.  Wide doors are needed to accommodate wheelchair riders entering fare-paid areas of transit terminals, as in this subway station in Rio de Janeiro.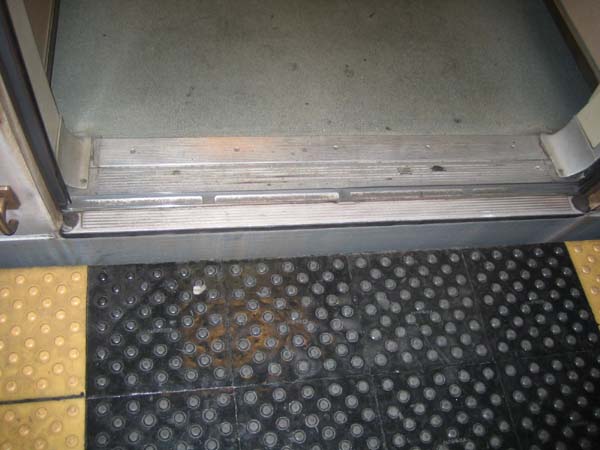  Everyone can safely board this BART train, due to a minimal horizontal and vertical gap.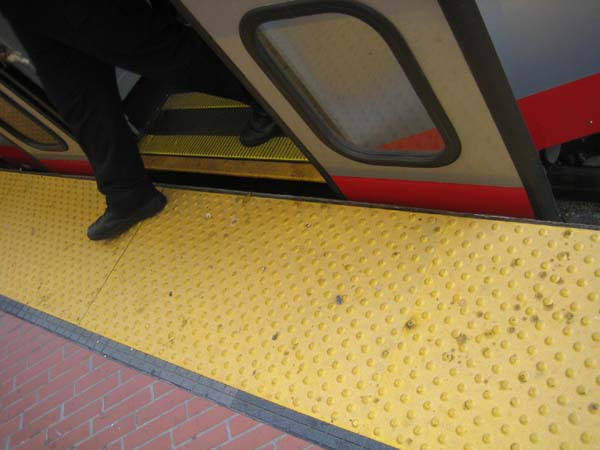  However, care must be taken that horizontal gaps are not too wide. The orange “gap filler” pops up when the doors open in San Francisco’s Muni Metro, assuring a safe gap.  Small portable ramps can provide inexpensive access in many rail stations, as shown here in Tokyo.  All passengers, and especially deaf and hard-of-hearing passengers, benefit from well-located visual information, as with this route display on board a train to the Hong Kong airport.  Advocates Anjlee Agarwal (left) and Sanjeev Sachdeva board the accessible Delhi Metro on its inaugural run.
Photo courtesy of Sanjay Sakaria and Samarthya, from Amar Ujjala Indian Daily  Express buses in Curitiba, Brazil, exemplify universal design. All passengers, including those with disabilities, quickly board with level entry. Similar Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) systems operate in Quito, Ecuador; Bogota, Colombia, and a growing number of cities around the world.
Photo by Charles Wright, Inter-American Development Bank.  Construction of this Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) trunk line corridor in Pereira, Colombia, symbolizes the rapid spread of BRT systems around the world. BRT systems lend themselves to universal design, but details must be monitored carefully to maximize accessibility.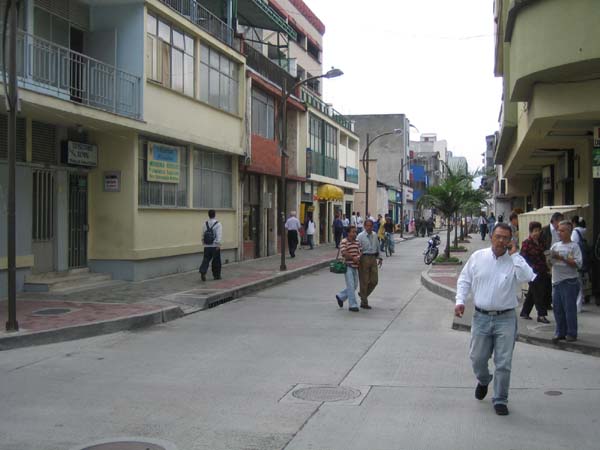  Although most BRT busways are on broad thoroughfares, this exclusive single-direction bus lane nearing completion in Pereira illustrates that BRT systems can sometimes be built on narrow streets.
This and above photo by T. Rickert courtesy of World Bank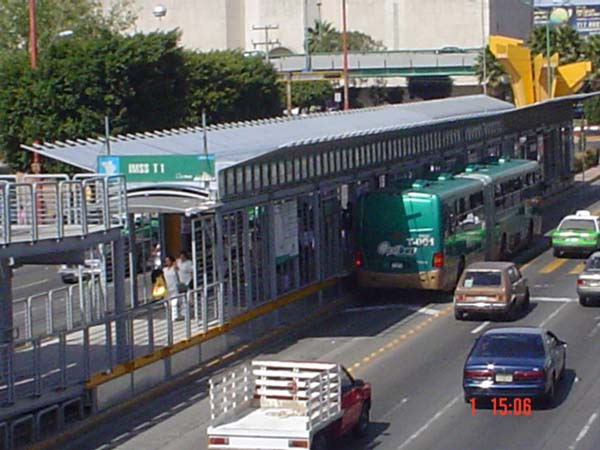  The photo shows an articulated bus docking at a Bus Rapid Transit station in León, Mexico.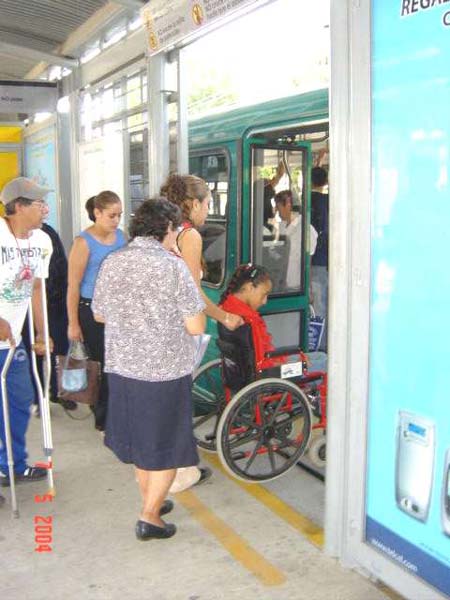  Pre-paid passengers inside a station board a high-capacity BRT bus in León.
This and above photo courtesy of Sistema Integrado de Transporte Masivo de León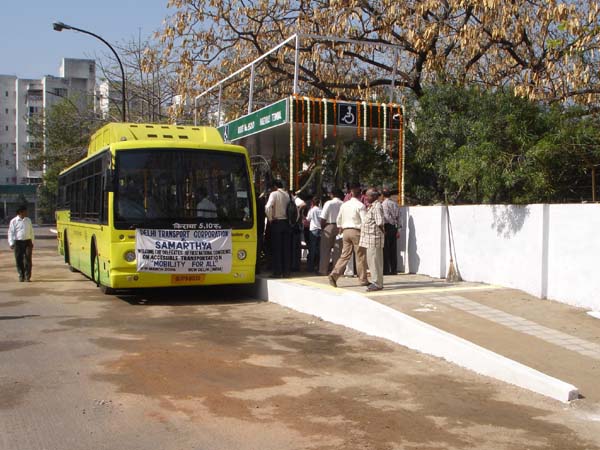  A prototype low-floor bus is tested in New Delhi adjacent to a platform the same height as the bus floor.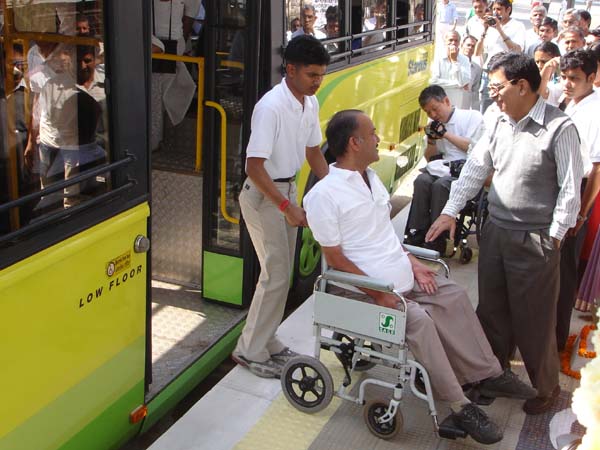  A closeup of the same bus stop illustrates the advantages of fast boarding for all passengers from platforms that eliminate the need for climbing steps to board.
This and above photo courtesy of Gerhard Menckhoff of the World Bank.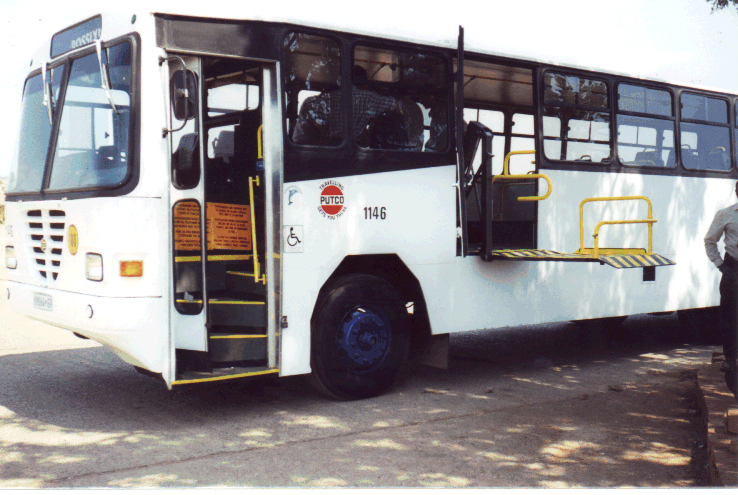  This prototype lift-equipped bus serves Mamelodi Township in South Africa. Note the excellent use of contrasting colors.
Photo by T. Rickert, courtesy of DFID (UK) and TRL (UK).  Mexico City officials inaugurated service in 2001 with 50 new buses equipped with lifts and other access features.
Photo courtesy of Marìa Eugenia Antunez.  In addition to a wheelchair lift, this bus in Mexico City has a retractable step beneath the front entrance.  This low-floor bus in Warsaw, Poland, uses an inexpensive hinged ramp which provides easy boarding for passengers with disabilities.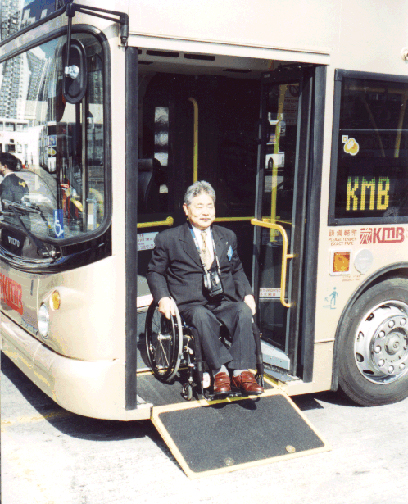  A low-floor bus in Hong Kong also exhibits excellent color contrast, using a bright yellow on key edges and surfaces.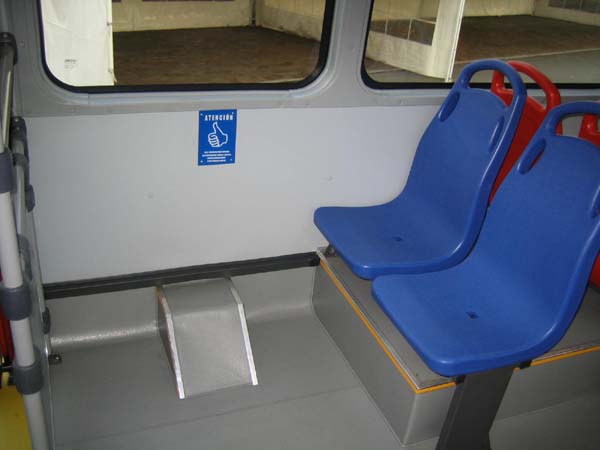  Transit systems around the world have reserved seating for seniors and passengers with disabilities, and often for pregnant women as well, as found on this TransMilenio bus in Bogotá, Colombia.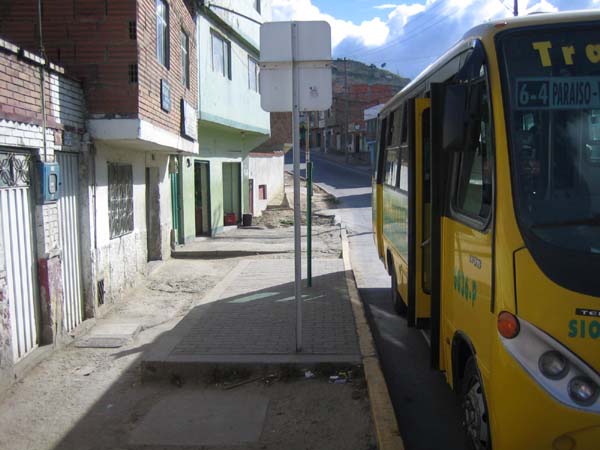  Even when bus stops are not accessible to wheelchair users, access for seniors and others with disabilities can be enhanced by a level all-weather pad even in the absence of paved sidewalks. The photo is from a TransMilenio feeder route in Bogotá.
This and above photo by T. Rickert courtesy of World Bank.  Thousands of Mexico City’s small inaccessible microbuses are being recycled and replaced with larger vehicles, often with better access features.  One such feature is this priority seating located behind the driver where there is extra leg room and it is easier for blind passengers to hear the driver call out key stops.
Photo by T. Rickert, courtesy of DFID (UK) and TRL (UK).  In other new buses in Mexico City, a wide rear door has low steps and is easily accessed by semi-ambulatory passengers from a raised sidewalk, but requires that drivers carefully pull in to the curb.
Photo by T. Rickert, courtesy of DFID (UK) and TRL (UK).  Community initiatives are playing a growing role in providing accessible door-to-door transport in many countries. This accessible van in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, belongs to the six-vehicle fleet of Persatuan Mobiliti.
Photo courtesy of Persatuan Mobiliti  Artist’s conception of a three-wheeled door-to-door vehicle connecting with an accessible ramped platform with bridge at a bus stop at a key site.  This prototype three-wheeled vehicle was built with AEI’s assistance by Kepha Motorbikes in Nairobi, Kenya. 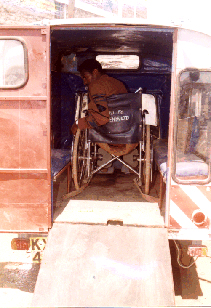 Detail showing entry via a ramp at the rear of the test vehicle.
This and above photo courtesy of Wycliffe Kepha.  This accessible bicycle rickshaw in India has a rear door which serves as a ramp.
Photo courtesy of Bikash Bharati Welfare Society and Lalita Sen.  A public meeting in Cali, Colombia, discusses accessibility to Bus Rapid Transit systems. Readers can go to the Bus Rapid Transit Accessibility Guidelines in our Resources section, under the links to the World Bank.
Photo by T. Rickert, courtesy of the World Bank.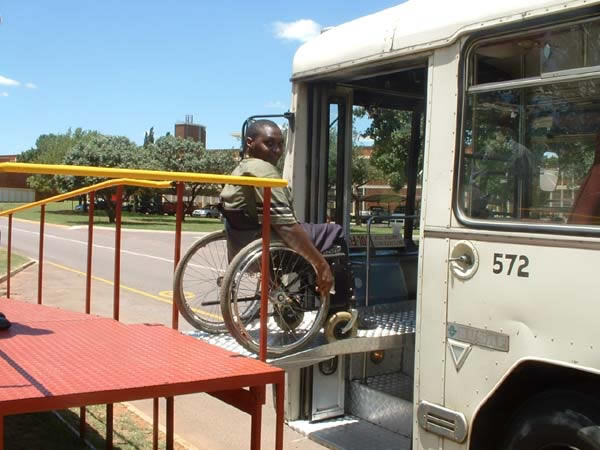  In this version, the bridge piece is mounted under the platform and put into place by the bus driver.
This and above photo courtesy of DFID (UK) and CSIR Transportek (South Africa).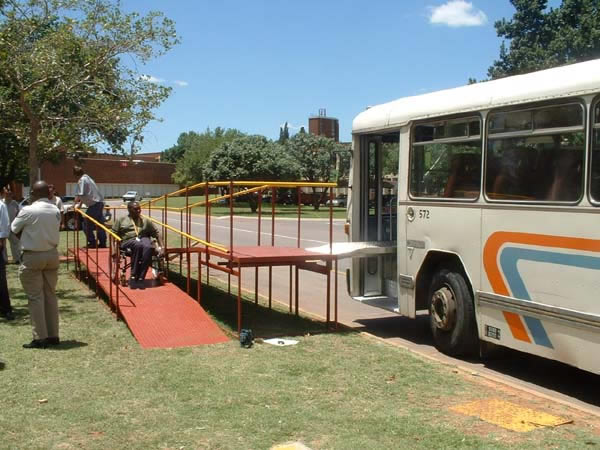  This test in South Africa of a prototype platform for use at key sites shows an alternative approach to access for wheelchair users.
|
|













































